Heat Pump Information
NRLP would like to ensure that you are informed as a consumer as to the best practices for using your heat pump.
Heat pumps are commonly used in Boone, particularly at apartment complexes.

Heat Pump Operation
The heat pump is a very efficient piece of equipment – today’s units are over 300% efficient as compared to a very good gas heater at 95-97%. It pumps heat from outside in during the winter and from inside out during the summer (like a refrigerator does).
Your Heat Pump, like any furnace, circulates and reheats room air. A heat pump is designed to give a low 25° boost to the air passing through, thus delivering about a 95° supply (70°+25°=95°). This lower supply temperature is high enough to heat the house, but is close to body temperature and can, at times, feel cool if you are sitting or standing in the air flow.
The Heat Pump may run longer to deliver the same amount of heat as a traditional furnace. When it gets close to 30° outside, the Heat Pump will run almost continuously. Remember that it is designed to do so. As the outside temperature drops to about 30° and below, the heat pump starts to need help from the backup (see more later in the article). Your thermostat will automatically add backup heat as needed in the most efficient way possible, and that proportion increases from no backup at around 30° to all backup at close to 0°. Remember that this happens without any help on your part.
Adjusting the Temperature
Raising a heat pump thermostat more than 1-2° at a time between reaching desired temperatures will actually raise your bill because it forces the more expensive/less efficient backup to come on when it would not normally be needed, trying to quickly “catch-up” on the desired heat. Be sure to set your thermostat on a comfortable temperature and not move it too much.
Using the “Emergency” Setting
The “emergency” switch/setting on your thermostat is for heating “emergencies.” It is designed to give you backup heat even if the Heat Pump is damaged or out of commission. When the switch is flipped/setting is selected, your efficient Heat Pump is shut off and the house heats only with the not-so-efficient backup, acting just like your toaster or oven. This will raise your heating costs (possibly significantly), so remember only to use the “emergency” switch/setting if your Heat Pump has a real emergency.
Heat Pump vs. Traditional Gas or Oil Furnace
A traditional gas/oil furnace feels warmer and will warm the air temperature more quickly, but is much less efficient since it directly burns fuel to CREATE heat. A Heat Pump uses much less fuel to MOVE/TRANSFER heat from outside in during the winter and from inside out during the summer.
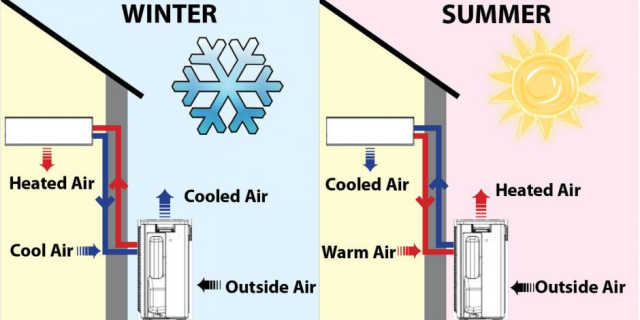
Diagram of how air circulates through a heat pump system